Nov 15, 2022 ·
newsletter

November 2022 Perhaps November conjures thoughts of holiday feasts and festivities, but for us, it’s the perfect time to chew the fat about machine learning! Make room on your plate for a peek behind the scenes into our current research on harnessing synthetic image generation to improve classification tasks. And, as usual, we reflect on our favorite reads of the month.
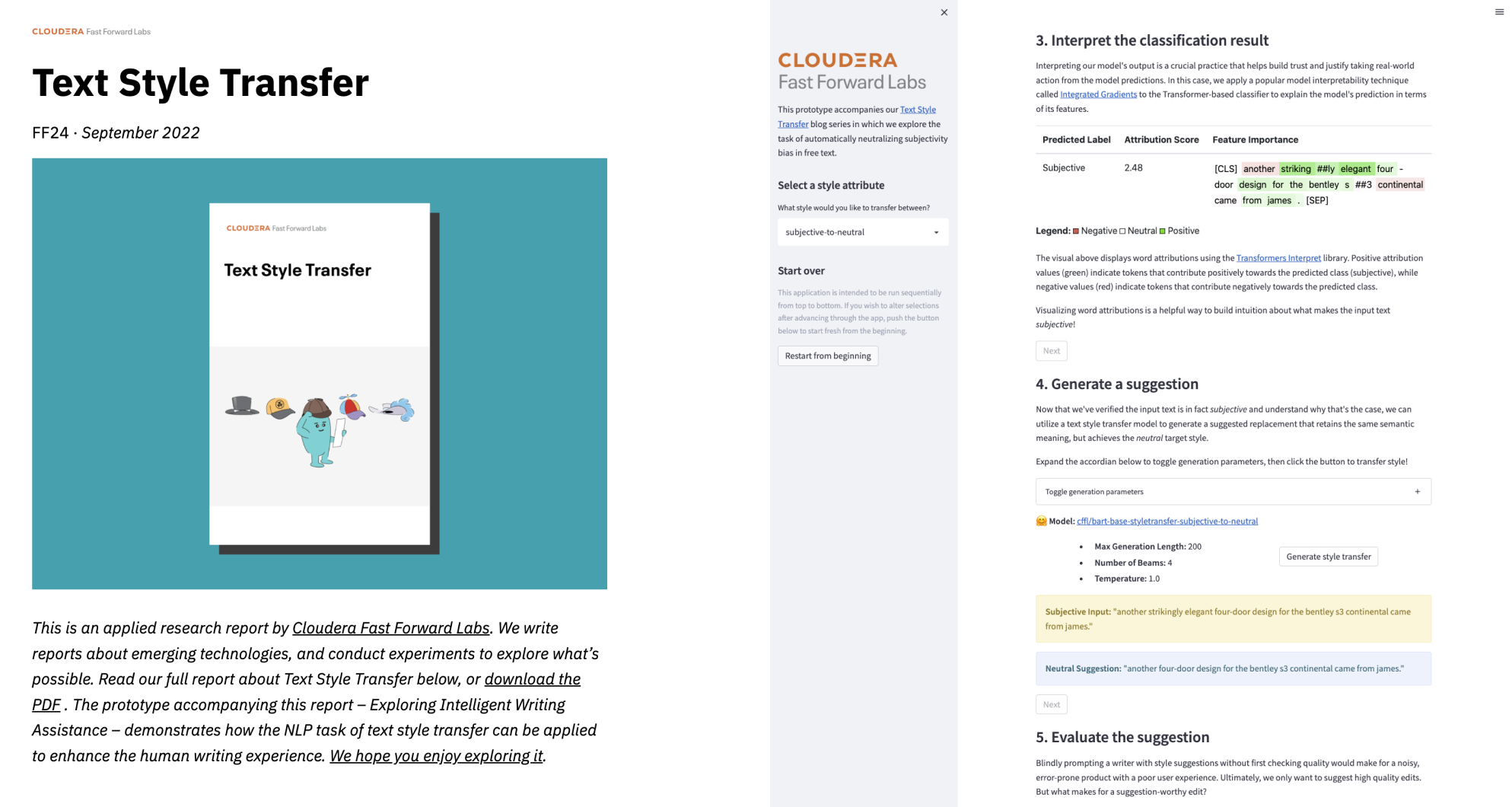
New Research! In the first half of this year, we focused on natural language processing with our Text Style Transfer blog series.
Nov 14, 2022 ·
post

by
Michael Gallaspy
·
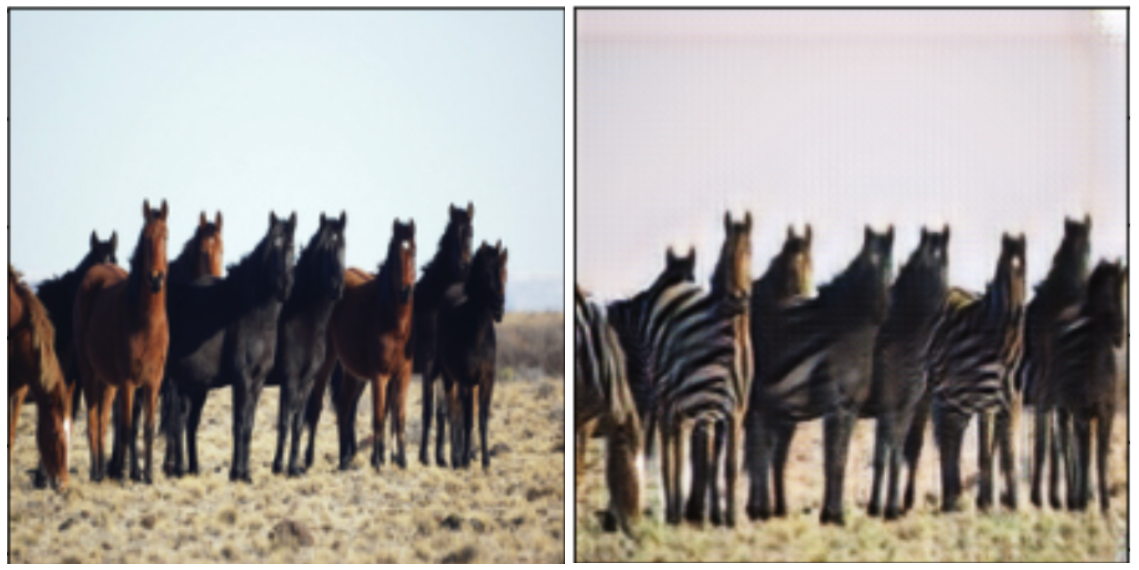
Introduction This post documents the first part of a research effort to quantify the impact of synthetic data augmentation in training a deep learning model for detecting manufacturing defects on steel surfaces. We chose to generate synthetic data using CycleGAN,1 an architecture involving several networks that jointly learn a mapping between two image domains from unpaired examples (I’ll elaborate below). Research from recent years has demonstrated improvement on tasks like defect detection2 and image segmentation3 by augmenting real image data sets with synthetic data, since deep learning algorithms require massive amounts of data, and data collection can easily become a bottleneck.
Oct 20, 2022 ·
newsletter

October 2022 We’ve got another action-packed newsletter for October! Highlights this month include the re-release of a classic CFFL research report, an example-heavy tutorial on Dask for distributed ML, and our picks for the best reads of the month.
Open Data Science Conference Cloudera Fast Forward Labs will be at ODSC West near San Fransisco on November 1st-3rd, 2022! If you’ll be in the Bay Area, don’t miss Andrew and Melanie who will be presenting our recent research on Neutralizing Subjectivity Bias with HuggingFace Transformers.
Sep 21, 2022 ·
newsletter
September 2022 Welcome to the September edition of the Cloudera Fast Forward Labs newsletter. This month we’re talking about ethics and we have all kinds of goodies to share including the final installment of our Text Style Transfer series and a couple of offerings from our newest research engineer. Throw in some choice must-reads and an ASR demo, and you’ve got yourself an action-packed newsletter!
New Research! Ethical Considerations When Designing an NLG System In the final post of our blog series on Text Style Transfer, we discuss some ethical considerations when working with natural language generation systems, and describe the design of our prototype application: Exploring Intelligent Writing Assistance.
Sep 8, 2022 ·
post
by
Michael Gallaspy
·
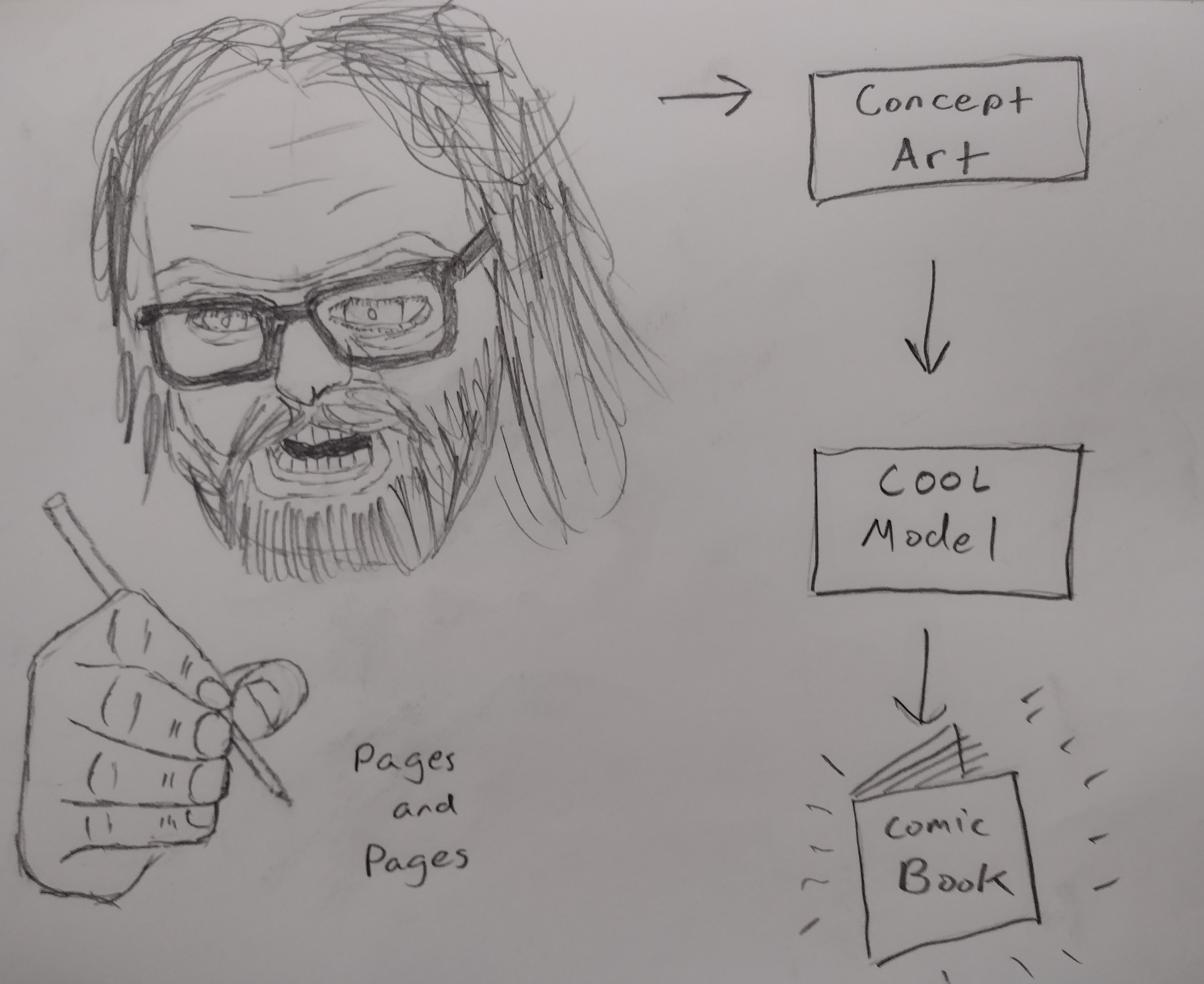
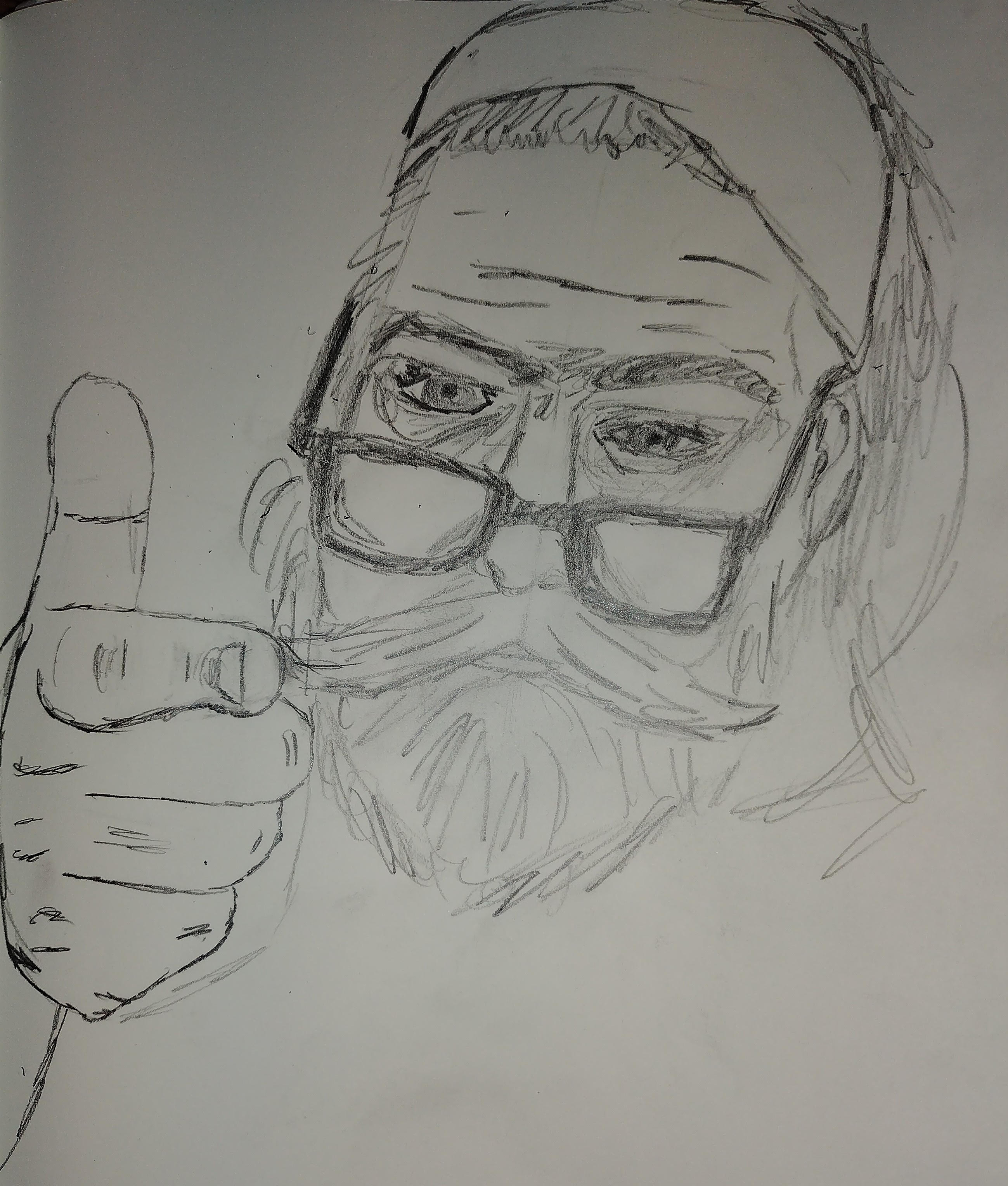
This post has a companion piece: Ethics Sheet for AI-assisted Comic Book Art Generation I want to make a comic book. Actually, I want to make tools for making comic books. See, the problem is, I can’t draw too good. I mean, I’m working on it. Check out these self portraits drawn 6 months apart:
Left: “Sad Face”. February 2022. Right: “Eyyyy”. August 2022. But I have a long way to go until my illustrations would be considered professional quality, notwithstanding the time it would take me to develop the many other skills needed for making comic books.
Aug 18, 2022 ·
newsletter

August 2022 Welcome to the August edition of the Cloudera Fast Forward Labs newsletter. This month we’re thrilled to introduce a new member of the FFL team, share TWO new applied machine learning prototypes we’ve built, and, as always, offer up some intriguing reads.
New Research Engineer! If you’re a regular reader of our newsletter, you likely noticed that we’ve been searching for new research engineers to join the Cloudera Fast Forward Labs team.